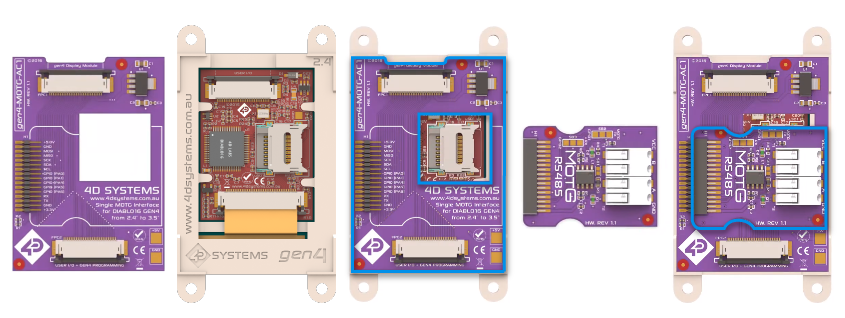
4D Systems’ MOTG-RS485 accessory module adds RS485 communication on your next display application.
RS485 holds significant importance in industrial applications due to its ability to facilitate long-distance communication. This serial communication method is designed to operate over extended cable distances. This makes it an ideal choice when devices are spread out over considerable distances within an industrial setting. RS485 communication is widely used in manufacturing, medical, retail, and commercial industries, even those involving high-quality display modules and processors.
When we say that the display processor does not support the RS485 serial communication method, it means that the system is limited from being used in scenarios where long-distance communication is required.
4D Systems has designed an accessory board for equipping various gen4-uLCD displays with an RS485 module. For example, the MOTG-AC1 can be used as an interface board to connect a MOTG module to Diablo16-based gen4 display modules easily. Similarly, we offer MOTG-AC2, MOTG-AC3, and MOTG-AC4 to feature single/dual MOTG slots depending on the module size and processor used.
In this article, we will discuss the fundamental aspects of RS485 and its relevance in industrial display applications. Furthermore, we will explore the innovative solution provided by 4D systems through their MOTG-RS485 accessory module in implementing RS485 serial communication support in all gen4 micro LCD displays.
Basics of RS485 serial communication protocol
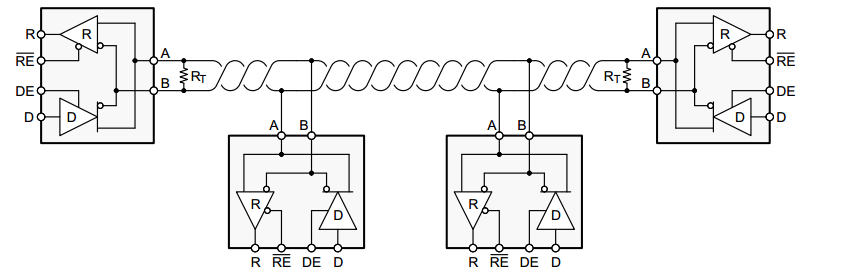
As mentioned earlier, RS485 communication is a serial communication method used for point-to-point communication among electrical devices, similar to USB and Ethernet, and is widely adopted in industrial applications. The RS485 communication method facilitates communication between a master and multiple slave devices in the network, where several slaves can be connected to the bus. While RS485 can support point-to-point communication, it is typically used with multiple slave devices.
Within the OSI model (Open Systems Interconnection) which defines the different layers of a communication system from the application to the physical layer, RS485 operates at the physical layer. The physical layer of the OSI model is responsible for facilitating data transfer between a device and a physical transmission medium.
The RS485 serial communication is not only for its long-distance data transmission capabilities but also for its resilience in electrically noisy environments. In RS485 communications, two types of noise can occur– differential noise and common mode noise.
While common mode noise generally has minimal impact, it is essential to implement the right circuit design techniques to minimize differential noise. In commercial applications, a twisted pair cable is used for RS485 communications to mitigate electrical interference. Each differential RS485 signal transceiver should be connected to the corresponding wires of the twisted pair, reducing the effects of electrical interference.
In a standard RS485 communication system using a twisted pair cable, the master device, acting as the host computer , initiates communication by sending a signal through its TX wire to establish a connection with the slave devices on the network. Subsequently, the master device transmits commands to the end device, for example, a motor controller to control speed or direction, which, in turn, receives the signal through its RX wire connected to the same twisted pair cable.
The RS485 communication offers versatility in display applications due to its advantages over other serial communication methods. 4D Systems has provided support to its gen4 micro LCD displays through the integration of the MOTG-RS485 accessory module into the advanced display system.
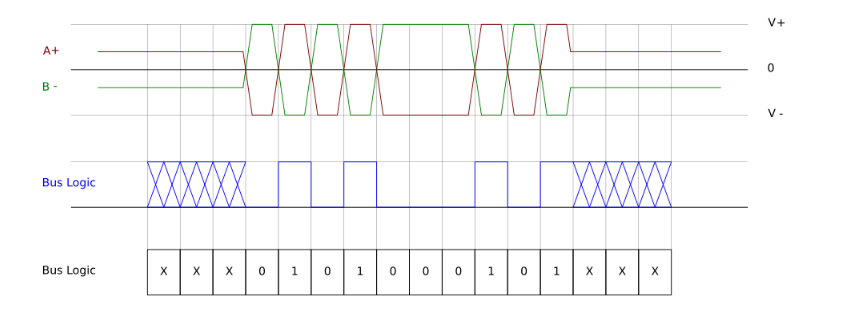
The above image depicts how an RS485 signal is observed on an oscilloscope. RS485 uses a differential signaling technique, where the same data is transmitted on two wires (A+ and B-) but with opposite polarities. When logic 1 is present on one wire, the other wire carries a logic 0.
To enable high-speed data transmission over long distances, these two opposing signals are transmitted through a twisted pair of wires. The advantage of this arrangement is that any noise induced on these lines affects both signals equally but in opposite directions, effectively canceling out the noise.
Add-on module to support RS485 communications
We developed the MOTG-RS485 module to offer a high-speed and low-cost solution that plays an important role in facilitating the integration of RS485 serial communication protocol in almost any of your intelligent display applications.
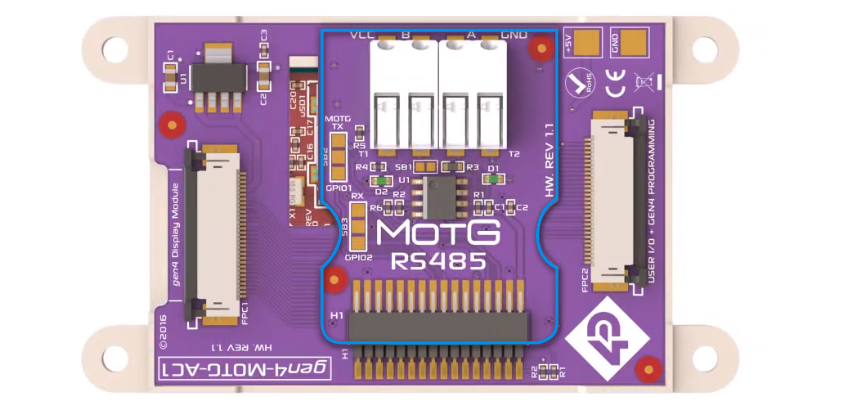
The MOTG-RS485 add-on module integrates the STMicroelectronics’ ST1480ACDR differential line transceiver, which operates using a 3.3V power supply for RS485 and RS422 communications. This transceiver configuration consists of a single driver and receiver, supporting half-duplex functionality. As a result, the module can alternate between transmitting and receiving data as required. With its robust capabilities, the transceiver enables reliable data transmission over long distances, even in electrically noisy environments.
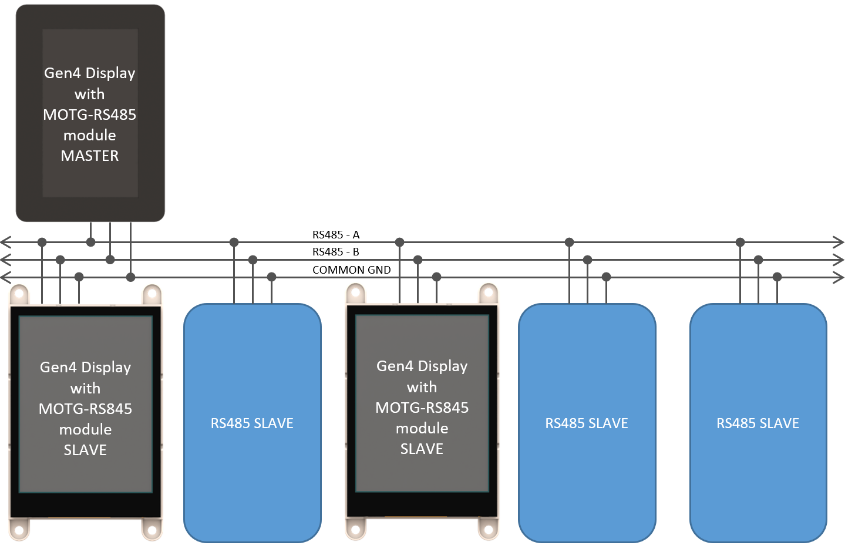
Master and Slaves (RS485)
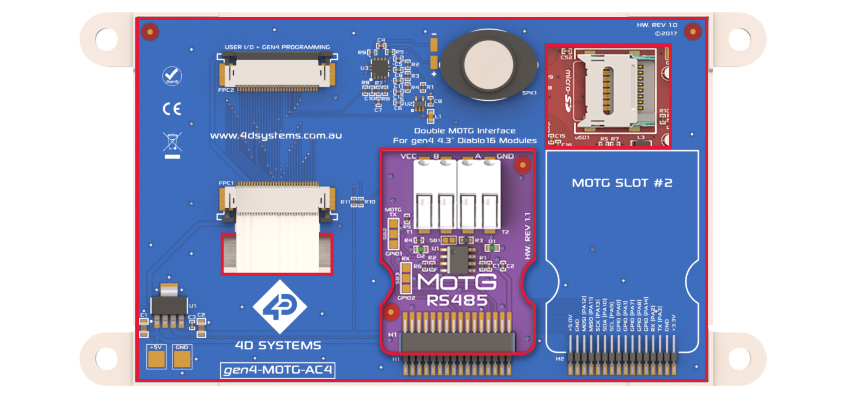
gen4 HMI 4.3″ Display Connected with the MOTG-AC4 Adaptor and MOTG-RS485 Module
What is 4D Systems’ MOTG approach?
4D Systems introduced the Modules-on-the-Go (MOTG) concept, enabling the seamless expansion of system capabilities for embedded designs involving display applications. This concept revolves around simple plug-and-play hardware modules that can be easily added or removed. This approach is aimed to eliminate the need for complex soldering, simplifying assembly and maintenance processes.
Conclusion
There you go. Now you can get your hands on the 4D Systems Modules-on-the-Go (MOTG) and add support for Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, RS485, RS232, CANBUS, and MP3 audio sound to your next display application.
The 4Discovery Range is also available as an option that supports RS485.
Until next time.
Table of contents
Subscribe to our newsletter
Latest Case Studies

This case study unveils a practical application of embedded innovation, highlighting the process and outcomes of upgrading legacy systems in a technology-focused product line. Through strategic technological integration, the project not only uplifted product performance but also markedly improved customer satisfaction levels. The subsequent pages delve into various strategic and operational enhancements made, providing readers with a nuanced understanding of the concrete impacts and subtleties involved in a real-world, engineer-led embedded innovation initiative. A testament to blending traditional systems with modern innovation.

Duratec, specializing in liquid handling devices for various industries, aimed to simplify the control interfaces of their new product line. Partnering with 4D Systems, they integrated a touch display module enhancing user-centricity and operational efficiency. This transition replaced outdated control panels with an intuitive, modern interface without compromising on control capabilities via the RS232 interface. Three new devices were launched, improving user interactions through user-friendly touch displays, showcasing Duratec's commitment to innovation. This collaboration allowed for more straightforward control, monitoring, and interaction with Duratec's devices, ensuring a better user experience and meeting industry demands.

In the challenging process of creating an advanced 3D printer, BCN3D encountered an unexpected difficulty: finding an appropriate, user-friendly display module. Despite initial struggles, BCN3D discovered the solution in 4D Systems’ gen4 display modules. These modules offered superior resolution, processing power, and flexibility. Key to BCN3D's decision was the modules' easy integration via a serial connection and the Arduino-compatible library into their firmware. For its Sigma R17 3D printer, BCN3D upgraded to the gen4-ULCD-35DCT-CLB, a 3.5-inch Intelligent TFT-LCD display module with capacitive touch, further enhancing the user experience. The gen4 series of intelligent display modules perfectly matched BCN3D's requirements, offering innovative solutions in the sophisticated 3D printing space.